User Defined Functions in SQL Server
This article talks about user defined functions (UDF) in SQL Server, its benefits, type of UDF, and UDF parameters.
Like stored procedures, User Defined Functions play a very important role in SQL Server. Although there are differences between Stored Proc and UDF, UDF can be used to perform a complex logic, can accept parameters and return data. The result of the function can be used in select statements, where clause, in the join. This article creates, executes UDF on Northwind database. You can download the Northwind database here.
Type of SQL User Defined Functions
Scalar Function:
Scalar functions returns only scalar/single value. Which can be used in the Select statement, Where, Group By, Having clause. It returns a single data value of the type mentioned in the RETURNS clause.
Create Scalar function by using the below query
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE FUNCTION GetOrderTotal
(
@OrderID INT
)
RETURNS DECIMAL
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @Total DECIMAL
SELECT @Total = SUM([UnitPrice] * [Quantity])
FROM [Northwind].[dbo].[Order Details]
WHERE OrderID = @OrderID
RETURN @Total
END
GO
You can use below inline query, Select statement, Where clause to execute this function.
SELECT dbo.GetOrderTotal(10248)
//Select Statement
SELECT OrderID, CustomerID, ShipCountry,
dbo.GetOrderTotal(OrderID) AS 'Order Total' FROM Orders
//In where clause
SELECT OrderID, CustomerID, ShipCountry,
dbo.GetOrderTotal(OrderID) AS 'Order Total' FROM Orders
WHERE dbo.GetOrderTotal(OrderID) >= 500
Table Valued Functions
Table valued function introduced in SQL Server 2005. It returns a resultset as a form of the Table variable. This can be a good alternative to View as View does not allow parameters whereas Table Valued Functions allowed parameters.
The Table returned by UDF can be used in From clause whereas the result set returned by Stored Procedure cannot use in From clause.
The body of Table valued UDF is just an inline query that use Select statement and returns a resultset.
Create Table valued UDF by using the below query
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE FUNCTION CustomerProductDetails
(
@CustomerID NCHAR(5)
)
RETURNS TABLE
AS
RETURN
(
SELECT C.CustomerID, C.CompanyName, C.City, O.OrderID, O.OrderDate,
P.ProductName, OD.UnitPrice, OD.Quantity, OD.Discount FROM [Products] P
INNER JOIN [Order Details] OD ON P.ProductID = OD.ProductID
INNER JOIN Orders O ON O.OrderID = OD.OrderID
INNER JOIN Customers C ON C.CustomerID = O.CustomerID
WHERE C.CustomerID = @CustomerID
)
GO
You can use this function in From clause or in JOIN. For more details see Types of SQL Server JOINS
SELECT * FROM dbo.CustomerProductDetails('VINET')
//Join with Employee Table
SELECT E.EmployeeID, E.LastName, E.FirstName, E.Title,
CP.CustomerID, CP.CompanyName, CP.City,
CP.OrderID, CP.OrderDate, CP.EmployeeID,
CP.ProductName, CP.UnitPrice, CP.Quantity, CP.Discount
FROM [Employees] E
JOIN dbo.CustomerProductDetails('VINET') CP ON
CP.EmployeeID = E.EmployeeID
You will see the below output when you join Table valued function
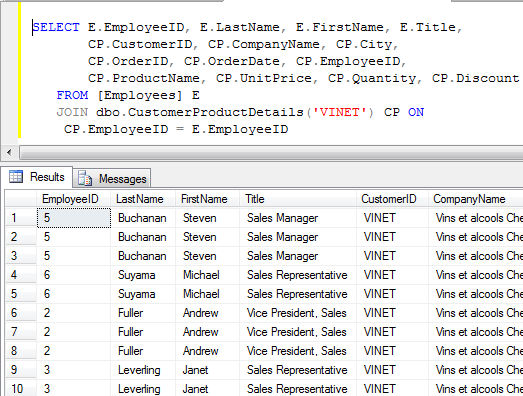
Multi-Statement Table Valued Function
A Multi-Statement Table-Valued user-defined function returns a table. It can execute one or more than one T-SQL statements. Body of function command you must define the table structure that is being returned. This type of UDF allows you to have more complex logic than Table Valued UDF. After creating this kind of UDF, you can use it in the FROM clause of a select statement unlike the behavior a stored procedure which can also return record sets.
Use the below query to create Multi Statement Table Valued Function.
CREATE FUNCTION CustomerOrderDetails
(
@CustomerID NCHAR(5)
)
RETURNS
@CustomerOrders table (
CustomerID NCHAR(5),
CompanyName NVARCHAR(40),
OrderID INT,
OrderDate DATETIME
)
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO @CustomerOrders
SELECT C.CustomerID, C.CompanyName, O.OrderID, O.OrderDate FROM
Customers C
INNER JOIN Orders O ON C.CustomerID = C.CustomerID
WHERE C.CustomerID = @CustomerID
IF @ROWCOUNT = 0
BEGIN
INSERT INTO @CustomerOrders
VALUES ('','No Orders Found',0,GETDATE())
END
RETURN
END
GO
Benefits of SQL User Defined Functions
-
The flexibility of using UDF output
SQL UDF can be executed through Select statements or inline queries. The select statement can show scalar UDF output as Select resultset.
Scalar functions can be used in SELECT, WHERE, HAVING clause, and Table valued functions can be used in FROM, JOIN, CROSS APPLY clause. See more examples about Cross Apply and Outer apply with examples -
Shorter Code
It gives the ability to write separate code blocks for complex logic and includes in the main query. This makes code less complex, easy to write, and maintain. -
Faster execution
Like stored procedures functions reduce compilation cost of T-SQL code by caching execution plan and reusing it for subsequent executions. It does not need to reparsed and re optimized with each execution resulting in much faster execution.
Limitations of SQL User Defined Functions
- Non-Deterministic Built-in Functions like GETDATE or RAND cannot be used in UDF.
- UDF return only one value or resultset. In stored procedure you can have multiple select statements to return multiple resultset however in UDF this is not possible.
- UDF can not call Stored Procedure, it can call only extended stored procedures.
- Dynamic SQL queries are now allowed in UDF.
- In UDF you cannot create Temporary tables.
- For XML is not supported in UDF.
- As UDF does not support error handling you cannot use RAISEERROR or @ERROR. You will have to handle errors in calling sql by using exception handling with try catch block.
Summary SQL UDFs are routines, it can perform complex logic, calculations, have one or more parameters and return either a scalar value or a Table datatype. This article shows to create various type of User Defined Functions and execute them.
Blog Search
-
Building Scalable Applications: Microservice Architecture Challenges
-
The Paradigm Shift to Low-Code and No-Code Development in Software Engineering
-
How To Use AutoMapper in ASP.NET Core Web API
-
Generate Log using Serilog And Seq In ASP.NET Core MVC 6
-
How to Setup CORS Policies in ASP.NET Core Web API
